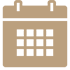
What Is The Plantar Fascia?
The plantar fascia is a thick band of connective tissue that runs along the bottom of the foot, from the heel bone to the base of the toes. It supports the arch of the foot and helps in various activities such as walking, running, and standing. The plantar fascia acts like a shock absorber, providing stability and helping with weight-bearing.
What Is Plantar Fasciitis?
Plantar fasciitis is one of the leading causes of heel pain. It is characterised by inflammation of the plantar fascia, causing stiffness and sharp pain in the heel upon awakening and during initial steps in the morning or after prolonged periods of sitting.
While plantar fasciitis can heal on its own, the process can be prolonged, causing significant discomfort.
For relief from plantar fasciitis, consult an orthopaedic specialist at 9711 8888.
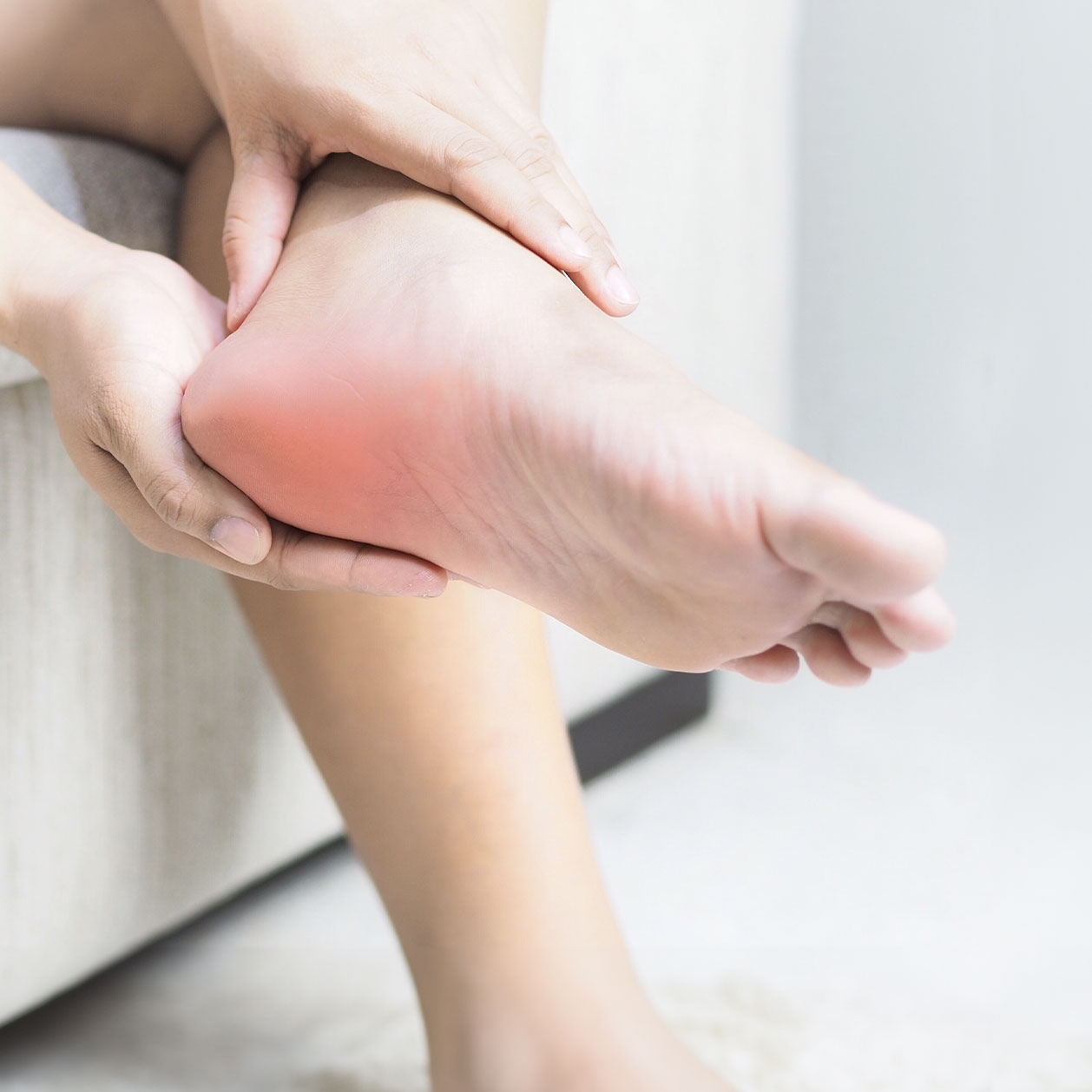
Signs and Symptoms of Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis typically manifests with specific symptoms that are primarily related to foot pain and discomfort, especially near the heel and arch area.
Common signs and symptoms of plantar fasciitis include:
- Stabbing Pain
in the bottom of the foot, often worse in the morning or after periods of rest.
- Stiffness And Limited Flexibility
in the foot, especially in the morning or after prolonged periods of inactivity.
- Tenderness Or Soreness
along the bottom of the foot, typically around the inner side of the heel.
- Swelling
in the heel or arch area of the foot.
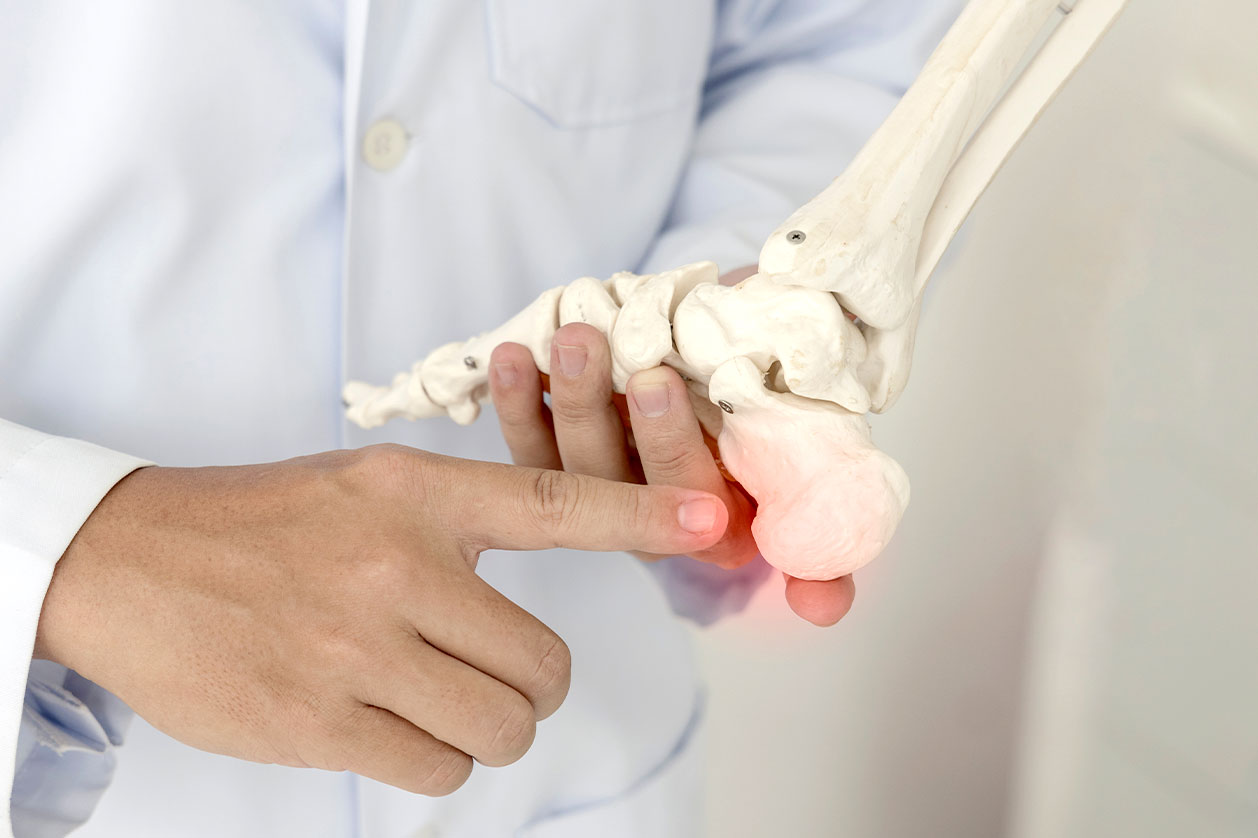
Common Causes of Plantar Fasciitis
If you experience pain when walking, rest until it subsides and do some gentle stretching afterwards. If symptoms persist, reach out to an orthopaedic specialist to avoid prolonged discomfort.
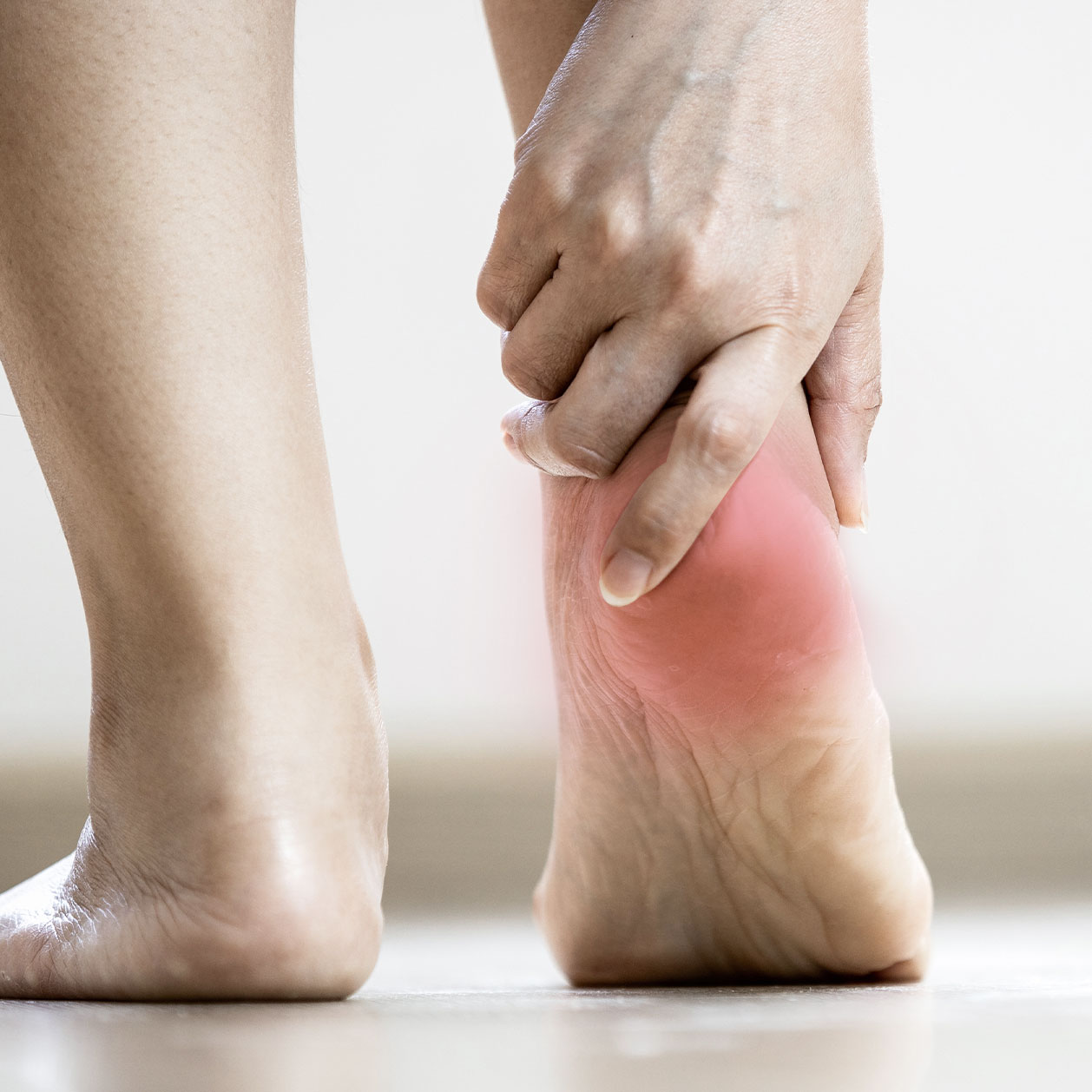
Plantar Fasciitis Risk Factors
Apart from the common causes, certain groups of people are more likely to develop plantar fasciitis, especially running enthusiasts. Other groups of people at higher risk include: